我正在尝试创建一个 ScrollView在 Kivy 中,小部件无限循环,就像我在网上找到的这个演示一样:
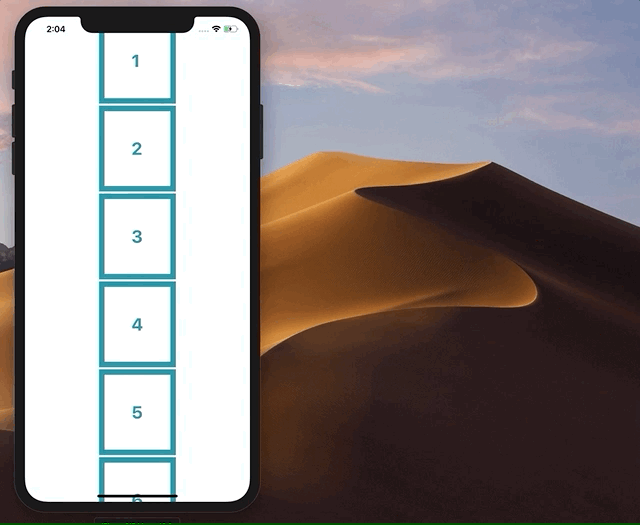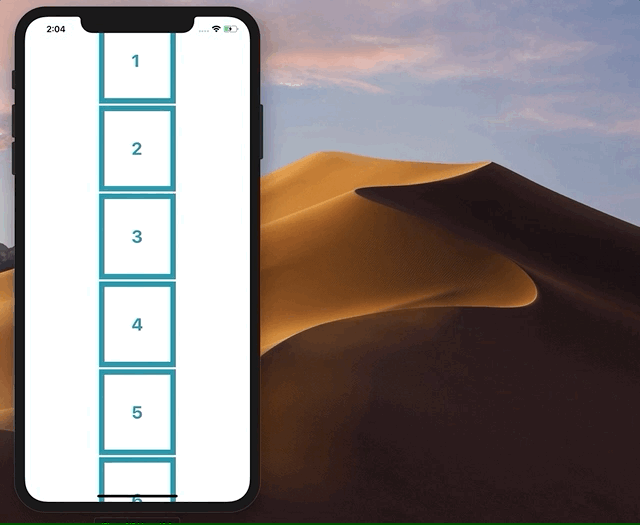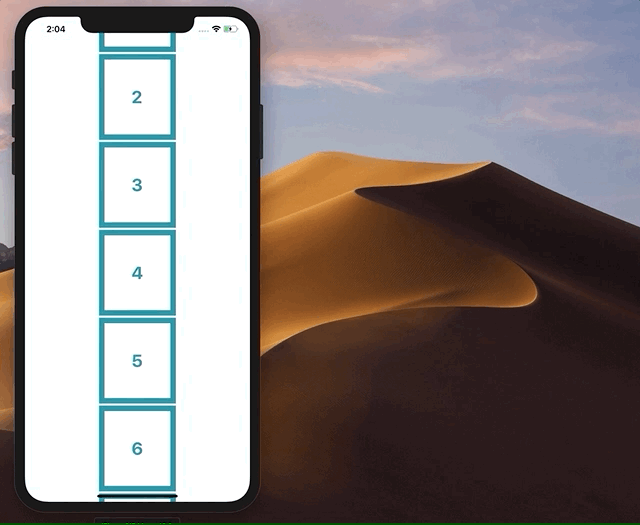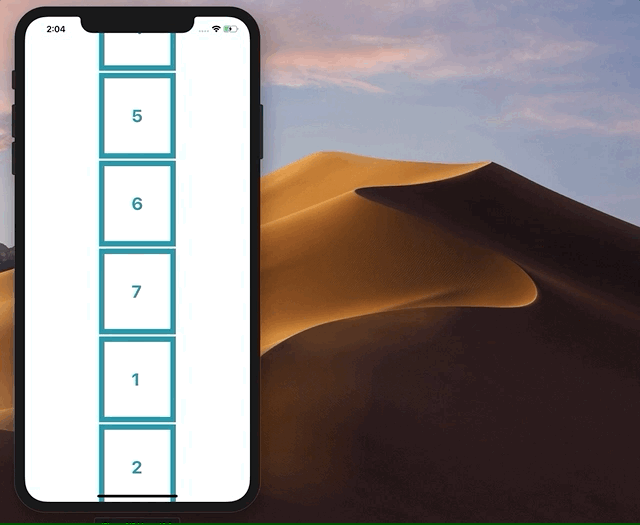
我试图删除 ScrollView 边界之外的小部件,并将它们添加回顶部或底部,具体取决于它们的原始位置。然而,这使整个应用程序闪烁和故障,最终无法正常工作。如果有人有实现这一目标的方法,将不胜感激!
最佳答案
我创建了一个基于 kivy 的自定义类 Stencilview和 RelativeLayout .
它的用法很像 kivy.uix.recycleview并支持循环。它有些未优化,但效果很好。没有 x 轴滚动(还)。应该能够处理无限量的数据而没有任何性能损失。 (使用 10.000.000 个数据条目进行测试 => 没有滞后))。
请不要引用我里面的任何内容 on_touch_down , on_touch_move , on_touch_up ,或其中调用的任何函数(唯一的异常(exception)是 scroll_y ),因为我不知道它们是如何工作的。
from functools import partial
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.clock import Clock
from kivy.compat import iteritems
from kivy.lang import Builder
from kivy.metrics import sp
from kivy.properties import DictProperty, ListProperty, NumericProperty, BooleanProperty, ObjectProperty
from kivy.uix.label import Label
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
from kivy.uix.stencilview import StencilView
from kivy.uix.widget import Widget
class LoopEntry(Widget):
data_index = NumericProperty(0)
data = DictProperty(None, allow_none=True)
hidden = BooleanProperty(False)
def is_hidden(self):
"""
:return:
"""
return self.hidden
def hide(self):
"""
:return:
"""
self.opacity = 0
self.hidden = True
def show(self):
"""
:return:
"""
self.opacity = 1
self.hidden = False
def update(self, data):
"""
overwrite this function if values other than attributes are needed
:param data:
:return:
"""
assert isinstance(data, dict)
# assign data
self.data = data
# apply values
for key, value in iteritems(data):
setattr(self, key, value)
class LoopContainer(RelativeLayout, StencilView):
pass
class LoopContainerDebug(RelativeLayout):
pass
class LoopScrollView(RelativeLayout):
"""
Main data source. Contains the data that needs to be exchanged.
Data can be manipulated without a whole redraw. Might cause unwanted behaviour
like blank lines and incorrect orders if not properly updated.
Setting this value causes a complete refresh.
"""
data = ListProperty()
"""
Children height. All children need to be the same height else
unwanted behaviour might occur.
Altering this value causes a complete refresh.
"""
children_height = NumericProperty(44)
"""
Amount of widgets added to the minimum widgets. (Very) Big numbers may cause lag.
Altering this value causes a complete refresh
"""
protection_amount = NumericProperty(4)
"""
viewclass is used to set the class type the widgets should be
future version might support manual adding of widgets
Altering this value causes a complete refresh.
"""
viewclass = ObjectProperty(LoopEntry)
"""
controls looping behaviour.
"""
loop = BooleanProperty(True)
"""
debugging option. shows hidden entries. not possible to switch
while running (yet)
"""
debug = BooleanProperty(False)
"""
scroll timeout. If the mouse has not been moved 'scroll_distance' within this time, dispatch the touch to children
in milliseconds
"""
scroll_timeout = NumericProperty(200)
"""
touch distance. Distance mouse needs to be moved
in pixel
"""
scroll_distance = NumericProperty('20dp')
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
"""
:param kwargs:
"""
# minimum widgets controls min/max amount of widgets on screen. Readonly.
self.__minimum_widgets = 0
# controls overscroll blocking if loop is disabled
self.__overscroll_block_y = "free"
# container
_kwargs = {
"size_hint": (None, None),
"size": (0, 0)
}
self.container = LoopContainer(**_kwargs) if not kwargs.get('debug', False) else LoopContainerDebug(**_kwargs)
# init super values
super(LoopScrollView, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# add container
self.add_widget(self.container)
# create widgets
self.__create_widgets()
# no idea
self._drag_touch = None
def on_pos(self, widget, value) -> None:
"""
:param widget:
:param value:
:return:
"""
def on_size(self, widget, value) -> None:
"""
:param widget:
:param value:
:return:
"""
# set container size
self.container.size = self.size
# recreate widgets
self.__create_widgets()
def on_data(self, widget, value) -> None:
"""
called if new data is set. Forces complete refresh. Use with care.
:param widget: widget event belongs to
:param value: event value
:return: None
"""
self.__create_widgets()
def on_protection_amount(self, widget, value) -> None:
"""
Forces complete refresh. Use with care.
:param widget: widget event belongs to
:param value: event value
:return: None
"""
self.__create_widgets()
def on_viewclass(self, widget, value) -> None:
"""
sets the viewclass used to entries
Forces complete refresh
:param widget: widget
:param value: value
:return: None
"""
self.__create_widgets()
def on_children_height(self, widget, value) -> None:
"""
Changes the children height.
Forces complete refresh.
:param widget: widget
:param value: value
:return: None
"""
self.__create_widgets()
def __create_widgets(self) -> None:
"""
clear all widgets and recreate
:return: None
"""
# remove all widgets
self.container.clear_widgets()
# calculate the minimum amount of required widgets
self.minimum_widgets = round(self.height / self.children_height) + self.protection_amount
# adding entries to the stencil view in reversed order to start with the smallest value (index 0) at top
for entry in range(self.minimum_widgets, 0, -1):
# create widget instance
_tmp_entry = self.viewclass(
size_hint=(1, None),
height=self.children_height,
pos=(0, self.height - self.children_height * entry)
)
# add to container
self.container.add_widget(_tmp_entry)
# refresh all widgets from given index and apply data values
self.__refresh_from_index(0)
def __refresh_from_index(self, index=0) -> None:
"""
refreshes widgets from given index
:param index: index to start with (very top entry)
:return: None
"""
# return if data is empty
if not self.data:
return
# reset widget positions to prevent weird behaviour
self.__reset_widget_positions(brute=True)
# reduce overhead. Slightly.
_data_length = len(self.data)
# loop through children and set values from given index
for child in self.container.children:
# if the current index exceeds the lengths and looping is disabled hide the widget
if index >= _data_length and not self.loop:
# Note : I dislike direct changing of values -_-
if not child.is_hidden():
child.hide() # hide child
child.data_index = index
else:
_normalized_index = index % _data_length
# get the new data value for the widget
_data_value = self.data[_normalized_index]
child.update(_data_value)
child.data_index = _normalized_index
if child.is_hidden():
child.show()
# increase index
index += 1
def __reset_widget_positions(self, brute=False) -> None:
"""
resets widget positions. Does not take into account values or
value positions.
If brute is True positions will be reset forcefully meaning data may mix up.
If brute is False positions will be scrolled meaning values will remain ordered.
:param brute: boolean
:return: None
"""
if brute:
# forcefully reset children
for child in self.container.children:
child.y = self.height - (child.height * (self.get_child_index(child) + 1))
else:
# get top child
_top_child = self.container.children[0]
# loop until child's y value matches the top threshold
while _top_child.y != self.height - _top_child.height:
# scroll by up to ensure proper order
self.scroll_y(1)
def __trigger_overscroll(self, entry: (LoopEntry, None), state):
"""
:param entry:
:param state:
:return:
"""
# trigger overscroll for down
if state == "bottom" and entry is not None:
# reset child to a proper spot
while entry.y != 0:
# scroll in the fastest direction
self.scroll_y(1 if entry.y < 0 else -1)
# set overscroll AFTER scrolling
self.__overscroll_block_y = "bottom"
# for up
elif state == "top" and entry is not None:
# reset child to proper spot
while entry.y != self.height - entry.height:
self.scroll_y(1 if entry.y < self.height - entry.height else 1)
# set overscroll AFTER scrolling
self.__overscroll_block_y = "top"
# reset else
else:
# free scrolling
self.__overscroll_block_y = "free"
def __update_entry(self, entry: LoopEntry, direction) -> None:
"""
:param entry:
:param direction:
:return:
"""
# get data length
_data_length = len(self.data)
# check direction
if direction == "down":
# get new index
_data_index = entry.data_index + self.minimum_widgets
if self.loop:
# normalize data index
_normalized_data_index = _data_index % _data_length
# update entry
entry.update(self.data[_normalized_data_index])
# set data index
entry.data_index = _normalized_data_index
# show entry
if entry.is_hidden():
entry.show()
else:
# if loop is disabled and data index exceeds either direction
if _data_index >= _data_length or _data_index < 0:
# hide children
if not entry.is_hidden():
entry.hide()
else:
# update entry from data index
entry.update(self.data[_data_index])
# show entry
if entry.is_hidden():
entry.show()
# set data index
entry.data_index = _data_index
elif direction == "up":
# get new data index
_data_index = entry.data_index - self.minimum_widgets
# if looping is enabled
if self.loop:
# normalize index
_normalized_data_index = _data_index % _data_length
# update entry
entry.update(self.data[_normalized_data_index])
# set data index
entry.data_index = _normalized_data_index
# show entry
if entry.is_hidden():
entry.show()
else:
if _data_index < 0 or _data_index >= _data_length:
# hide children
if not entry.is_hidden():
entry.hide()
else:
# update entry from data index
entry.update(self.data[_data_index])
# show entry
if entry.is_hidden():
entry.show()
# set data index
entry.data_index = _data_index
else:
# error
raise Exception
def get_child_index(self, child) -> (int, None):
"""
returns the index if the child exists in list else None
:param child: child instance
:return: int,None
"""
return self.container.children.index(child) if child in self.container.children else None
def scroll_y(self, delta_y) -> None:
"""
scroll by given amount
:param delta_y: delta value in pixels
:return: None
"""
# set highest and lowest children (needed for rotation)
_highest, _lowest = self.container.children[0], self.container.children[0]
# round delta y
delta_y = round(delta_y)
# get data length
data_length = len(self.data)
# control var
_free_block = True
# loop through children
for child in self.container.children:
# increase/decrease children y position
child.y += delta_y
# update highest and lowest children
_highest = child if child.y > _highest.y else _highest
_lowest = child if child.y < _lowest.y else _lowest
# check for loop condition
if not self.loop:
# if current child's index exceeds or evens data length and is higher than given
# threshold trigger overscroll event for bottom
if child.data_index >= data_length - 1 and child.y >= 0:
self.__trigger_overscroll(child, 'bottom')
_free_block = False
# if current child's index is smaller or evens 0 and is higher than the given
# threshold trigger overscroll event for top
elif child.data_index <= 0 and child.y <= self.height - child.height:
self.__trigger_overscroll(child, 'top')
_free_block = False
# unblock if block is free to be unblocked
if _free_block:
self.__trigger_overscroll(None, 'reset')
# check if swap is needed
if _highest.y > self.height + _highest.height and delta_y > 0:
# set new y for highest if it exceeds max height
_highest.y = _lowest.y - _highest.height
self.__update_entry(_highest, direction="down")
elif _lowest.y < 0 - _lowest.height - _lowest.height and delta_y < 0:
_lowest.y = _highest.y + _highest.height
self.__update_entry(_lowest, direction="up")
def _get_uid(self, prefix='sv'):
return '{0}.{1}'.format(prefix, self.uid)
def on_touch_down(self, touch):
x, y = touch.pos
if not self.collide_point(x, y):
touch.ud[self._get_uid('svavoid')] = True
return super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_down(touch)
if self._drag_touch or ('button' in touch.profile and touch.button.startswith('scroll')):
return super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_down(touch)
# no mouse scrolling, so the user is going to drag with this touch.
self._drag_touch = touch
uid = self._get_uid()
touch.grab(self)
touch.ud[uid] = {
'mode': 'unknown',
'dx': 0,
'dy': 0
}
Clock.schedule_once(self._change_touch_mode, self.scroll_timeout / 1000.)
return True
def on_touch_move(self, touch):
if self._get_uid('svavoid') in touch.ud or self._drag_touch is not touch:
return super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_move(touch) or self._get_uid() in touch.ud
if touch.grab_current is not self:
return True
uid = self._get_uid()
ud = touch.ud[uid]
mode = ud['mode']
if mode == 'unknown':
ud['dx'] += abs(touch.dx)
ud['dy'] += abs(touch.dy)
if ud['dx'] > sp(self.scroll_distance):
mode = 'drag'
if ud['dy'] > sp(self.scroll_distance):
mode = 'drag'
ud['mode'] = mode
if mode == 'drag':
if (touch.dy > 0 and self.__overscroll_block_y == "bottom" or
touch.dy < 0 and self.__overscroll_block_y == "top"):
pass
else:
self.scroll_y(touch.dy)
return True
def on_touch_up(self, touch):
if self._get_uid('svavoid') in touch.ud:
return super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_up(touch)
if self._drag_touch and self in [x() for x in touch.grab_list]:
touch.ungrab(self)
self._drag_touch = None
ud = touch.ud[self._get_uid()]
if ud['mode'] == 'unknown':
super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_down(touch)
Clock.schedule_once(partial(self._do_touch_up, touch), .1)
else:
if self._drag_touch is not touch:
super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_up(touch)
return self._get_uid() in touch.ud
def _do_touch_up(self, touch, *largs):
super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_up(touch)
# don't forget about grab event!
for x in touch.grab_list[:]:
touch.grab_list.remove(x)
x = x()
if not x:
continue
touch.grab_current = x
super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_up(touch)
touch.grab_current = None
def _change_touch_mode(self, *largs):
if not self._drag_touch:
return
uid = self._get_uid()
touch = self._drag_touch
ud = touch.ud[uid]
if ud['mode'] != 'unknown':
return
touch.ungrab(self)
self._drag_touch = None
touch.push()
touch.apply_transform_2d(self.parent.to_widget)
super(LoopScrollView, self).on_touch_down(touch)
touch.pop()
return
# ------------------ Showcase ------------------ #
from kivy.uix.button import Button
class LoopLabel(LoopEntry, Label):
pass
class LoopButton(LoopEntry, Button):
pass
__style = ("""
<LoopLabel>:
color : 1,1,1
text: "test"
canvas:
Color:
rgb : 1,1,1
Line:
rectangle: (*self.pos,self.width ,self.height )
<LoopContainer,LoopContainerDebug>:
canvas:
Color:
rgb : 1,0,0
Line:
rectangle: (0+1,0+1,self.width - 1,self.height -1 )
width:5
""")
class InfiniteScrollingScrollView(App):
def build(self):
root = RelativeLayout()
root.bind(on_touch_down=lambda x, y: print("-" * 10))
sv = LoopScrollView(
size_hint=(0.5, 0.5), pos_hint={'center': (0.5, 0.5)}, viewclass=LoopLabel, debug=False
)
sv.data = [{'text': str(x)} for x in range(10000000)]
root.add_widget(sv)
return root
if __name__ == "__main__":
Builder.load_string(__style)
InfiniteScrollingScrollView().run()
关于python-3.x - Kivy 无限循环 ScrollView ,我们在Stack Overflow上找到一个类似的问题: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/68084971/