我正在尝试编写一个可以像 DnD、Munchkin 等一样掷骰子的计算器。所以我需要计算像 2*(2d5+3d7) 这样的表达式,我应该 2d5 代表用 5 个面滚动 2 个骰子的结果。我以一个原始计算器为基础,它可以工作。现在我正在尝试使用语义操作添加滚动规则。我想调用roll每次出现表达式 XdY 时函数并将其结果添加到当前值。但似乎我不能只做_val+=roll(dice_number, dice_value)在语义 Action 中。那么,这样做的方法是什么?完整代码在这里:
#define BOOST_SPIRIT_NO_PREDEFINED_TERMINALS
#define BOOST_BIND_GLOBAL_PLACEHOLDERS
#include <boost/config/warning_disable.hpp>
#include <boost/spirit/include/qi.hpp>
#include <boost/spirit/include/phoenix_core.hpp>
#include <boost/spirit/include/phoenix_operator.hpp>
#include <boost/spirit/include/phoenix_stl.hpp>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/phoenix/bind/bind_function.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#include <boost/random.hpp>
std::time_t now = std::time(0);
boost::random::mt19937 gen{static_cast<std::uint32_t>(now)};
int roll(int dice_number, int dice_value, int use_crits=false)
{
int res=0;
boost::random::uniform_int_distribution<> dist{1, value};
for(int i=0; i<dice_number; i++)
{
res+=dist(gen);
}
return res;
}
namespace client
{
namespace qi = boost::spirit::qi;
namespace ascii = boost::spirit::ascii;
using boost::phoenix::push_back;
using boost::phoenix::ref;
//calculator grammar
template <typename Iterator>
struct calculator : qi::grammar<Iterator, int(), ascii::space_type>
{
calculator() : calculator::base_type(expression)
{
qi::_val_type _val;
qi::_1_type _1, _2;
qi::uint_type uint_;
qi::int_type int_;
int dice_num, dice_value;
roll =
(int_ [ref(dice_num)=_1]>> 'd' >> int_ [ref(dice_value)=_1]) [_val+=roll(dice_num, dice_value)] ;//The problem is here
expression =
term [_val = _1]
>> *( ('+' >> term [_val += _1])
| ('-' >> term [_val -= _1])
)
;
term =
factor [_val = _1]
>> *( ('*' >> factor [_val *= _1])
| ('/' >> factor [_val /= _1])
)
;
factor =
roll [_val=_1]
| uint_ [_val = _1]
| '(' >> expression [_val = _1] >> ')'
| ('-' >> factor [_val = -_1])
| ('+' >> factor [_val = _1])
;
}
qi::rule<Iterator, int(), ascii::space_type> roll, expression, term, factor;
};
}
int
main()
{
std::cout << "/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////\n\n";
std::cout << "Expression parser...\n\n";
std::cout << "/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////\n\n";
std::cout << "Type an expression...or [q or Q] to quit\n\n";
typedef std::string::const_iterator iterator_type;
typedef client::calculator<iterator_type> calculator;
boost::spirit::ascii::space_type space; // skipper
calculator calc; // grammar
std::string str;
int result;
while (std::getline(std::cin, str))
{
if (str.empty() || str[0] == 'q' || str[0] == 'Q')
break;
std::string::const_iterator iter = str.begin();
std::string::const_iterator end = str.end();
bool r = phrase_parse(iter, end, calc, space, result);
if (r && iter == end)
{
std::cout << "-------------------------\n";
std::cout << "Parsing succeeded\n";
std::cout << "result = " << result << std::endl;
std::cout << "-------------------------\n";
}
else
{
std::string rest(iter, end);
std::cout << "-------------------------\n";
std::cout << "Parsing failed\n";
std::cout << "stopped at: \" " << rest << "\"\n";
std::cout << "-------------------------\n";
}
}
std::cout << "Bye... :-) \n\n";
return 0;
}
最佳答案
语义 Action 是“延迟 Actor ”。含义:它们是描述函数调用的函数对象,在规则定义期间它们不会被调用。
所以你可以使用
使用凤凰绑定(bind),因为它最接近您的代码:
roll = (qi::int_ >> 'd' >> qi::int_)
[ _val = px::bind(::roll, _1, _2) ] ;
- Note how I removed the use of local variables. They would have been UB because they don't exist after the constructor completes!
- Note also that I needed to disambiguate
::rollwith a global namespace qualification, because therollrule member shadows it.
Live Demo
//#define BOOST_SPIRIT_DEBUG
#include <boost/spirit/include/qi.hpp>
#include <boost/spirit/include/phoenix.hpp>
static int roll_dice(int num, int faces);
namespace Parser {
namespace qi = boost::spirit::qi;
namespace px = boost::phoenix;
//calculator grammar
template <typename Iterator>
struct calculator : qi::grammar<Iterator, int()> {
calculator() : calculator::base_type(start) {
using namespace qi::labels;
start = qi::skip(qi::space) [ expression ];
roll = (qi::int_ >> 'd' >> qi::int_)
[ _val = px::bind(::roll_dice, _1, _2) ] ;
expression =
term [_val = _1]
>> *( ('+' >> term [_val += _1])
| ('-' >> term [_val -= _1])
)
;
term =
factor [_val = _1]
>> *( ('*' >> factor [_val *= _1])
| ('/' >> factor [_val /= _1])
)
;
factor
= roll [_val = _1]
| qi::uint_ [_val = _1]
| '(' >> expression [_val = _1] >> ')'
| ('-' >> factor [_val = -_1])
| ('+' >> factor [_val = _1])
;
BOOST_SPIRIT_DEBUG_NODES((start)(roll)(expression)(term)(factor))
}
private:
qi::rule<Iterator, int()> start;
qi::rule<Iterator, int(), qi::space_type> roll, expression, term, factor;
};
}
#include <random>
#include <iomanip>
static int roll_dice(int num, int faces) {
static std::mt19937 gen{std::random_device{}()};
int res=0;
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dist{1, faces};
for(int i=0; i<num; i++) {
res+=dist(gen);
}
return res;
}
int main() {
using It = std::string::const_iterator;
Parser::calculator<It> const calc;
for (std::string const& str : {
"42",
"2*(2d5+3d7)",
})
{
auto f = str.begin(), l = str.end();
int result;
if (parse(f, l, calc, result)) {
std::cout << "result = " << result << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Parsing failed\n";
}
if (f != l) {
std::cout << "Remaining input: " << std::quoted(std::string(f, l)) << "\n";
}
}
}
打印品,例如
result = 42
result = 38
错误!
先说正确。你可能没有意识到
uniform_int_distribution<>(a,b) 导致UB¹如果 b<a .当有人键入
-7d5 时类似.您需要添加检查:
static int roll_dice(int num, int faces) {
if (num < 0) throw std::range_error("num");
if (faces < 1) throw std::range_error("faces");
int res = 0;
static std::mt19937 gen{ std::random_device{}() };
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dist{ 1, faces };
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
res += dist(gen);
}
std::cerr << "roll_dice(" << num << ", " << faces << ") -> " << res << "\n";
return res;
}
Defensive Programming is a must in any domain/language. In C++ it protects against Nasal Demons
概括!
该代码已大大简化,我添加了必要的管道以获得调试输出:
<start>
<try>2*(2d5+3d7)</try>
<expression>
<try>2*(2d5+3d7)</try>
<term>
<try>2*(2d5+3d7)</try>
<factor>
<try>2*(2d5+3d7)</try>
<roll>
<try>2*(2d5+3d7)</try>
<fail/>
</roll>
<success>*(2d5+3d7)</success>
<attributes>[2]</attributes>
</factor>
<factor>
<try>(2d5+3d7)</try>
<roll>
<try>(2d5+3d7)</try>
<fail/>
</roll>
<expression>
<try>2d5+3d7)</try>
<term>
<try>2d5+3d7)</try>
<factor>
<try>2d5+3d7)</try>
<roll>
<try>2d5+3d7)</try>
<success>+3d7)</success>
<attributes>[9]</attributes>
</roll>
<success>+3d7)</success>
<attributes>[9]</attributes>
</factor>
<success>+3d7)</success>
<attributes>[9]</attributes>
</term>
<term>
<try>3d7)</try>
<factor>
<try>3d7)</try>
<roll>
<try>3d7)</try>
<success>)</success>
<attributes>[10]</attributes>
</roll>
<success>)</success>
<attributes>[10]</attributes>
</factor>
<success>)</success>
<attributes>[10]</attributes>
</term>
<success>)</success>
<attributes>[19]</attributes>
</expression>
<success></success>
<attributes>[19]</attributes>
</factor>
<success></success>
<attributes>[38]</attributes>
</term>
<success></success>
<attributes>[38]</attributes>
</expression>
<success></success>
<attributes>[38]</attributes>
</start>
result = 38
现在,让我们从概念上看一下语法。真的,
d只是一个二元中缀运算符,如 3+7或 3d7 .因此,如果我们假设它与一元加/减具有相同的优先级,我们可以简化规则,同时使语法更加通用:factor = (qi::uint_ [_val = _1]
| '(' >> expression [_val = _1] >> ')'
| ('-' >> factor [_val = -_1])
| ('+' >> factor [_val = _1])
) >> *(
'd' >> factor [_val = px::bind(::roll_dice, _val, _1)]
)
;
哎呀!没有了
roll规则。此外,突然以下成为有效输入:1*3d(5+2)
(3+9*3)d8
0*0d5
(3d5)d15
1d(15d3)
(1d1d1d1) * 42
完整演示
Live On Coliru
//#define BOOST_SPIRIT_DEBUG
#include <boost/spirit/include/qi.hpp>
#include <boost/spirit/include/phoenix.hpp>
static int roll_dice(int num, int faces);
namespace Parser {
namespace qi = boost::spirit::qi;
namespace px = boost::phoenix;
//calculator grammar
template <typename Iterator>
struct calculator : qi::grammar<Iterator, int()> {
calculator() : calculator::base_type(start) {
using namespace qi::labels;
start = qi::skip(qi::space) [ expression ];
expression =
term [_val = _1]
>> *( ('+' >> term [_val += _1])
| ('-' >> term [_val -= _1])
)
;
term =
factor [_val = _1]
>> *( ('*' >> factor [_val *= _1])
| ('/' >> factor [_val /= _1])
)
;
factor = (qi::uint_ [_val = _1]
| '(' >> expression [_val = _1] >> ')'
| ('-' >> factor [_val = -_1])
| ('+' >> factor [_val = _1])
) >> *(
'd' >> factor [_val = px::bind(::roll_dice, _val, _1)]
)
;
BOOST_SPIRIT_DEBUG_NODES((start)(expression)(term)(factor))
}
private:
qi::rule<Iterator, int()> start;
qi::rule<Iterator, int(), qi::space_type> expression, term, factor;
};
}
#include <random>
#include <iomanip>
static int roll_dice(int num, int faces) {
if (num < 0) throw std::range_error("num");
if (faces < 1) throw std::range_error("faces");
int res = 0;
static std::mt19937 gen{ std::random_device{}() };
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dist{ 1, faces };
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
res += dist(gen);
}
std::cerr << "roll_dice(" << num << ", " << faces << ") -> " << res << "\n";
return res;
}
int main() {
using It = std::string::const_iterator;
Parser::calculator<It> const calc;
for (std::string const& input : {
"42",
"2*(2d5+3d7)",
// generalized
"1*3d(5+2)",
"(3+9*3)d8",
"0*0d5",
"(3d5)d15",
"1d(15d3)",
"(1d1d1d1) * 42",
})
{
std::cout << "\n==== Parsing " << std::quoted(input) << "\n";
auto f = input.begin(), l = input.end();
int result;
if (parse(f, l, calc, result)) {
std::cout << "Parse result = " << result << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Parsing failed\n";
}
if (f != l) {
std::cout << "Remaining input: " << std::quoted(std::string(f, l)) << "\n";
}
}
}
打印
¹你不喜欢 C++ 吗?
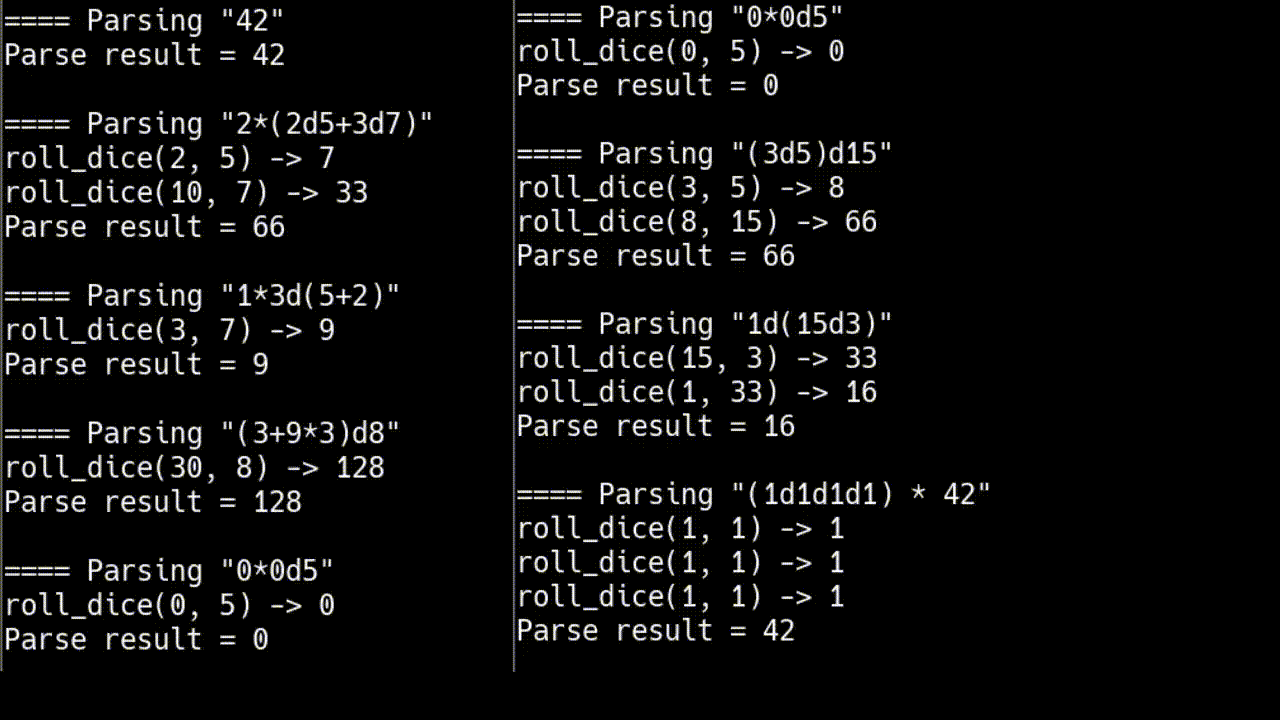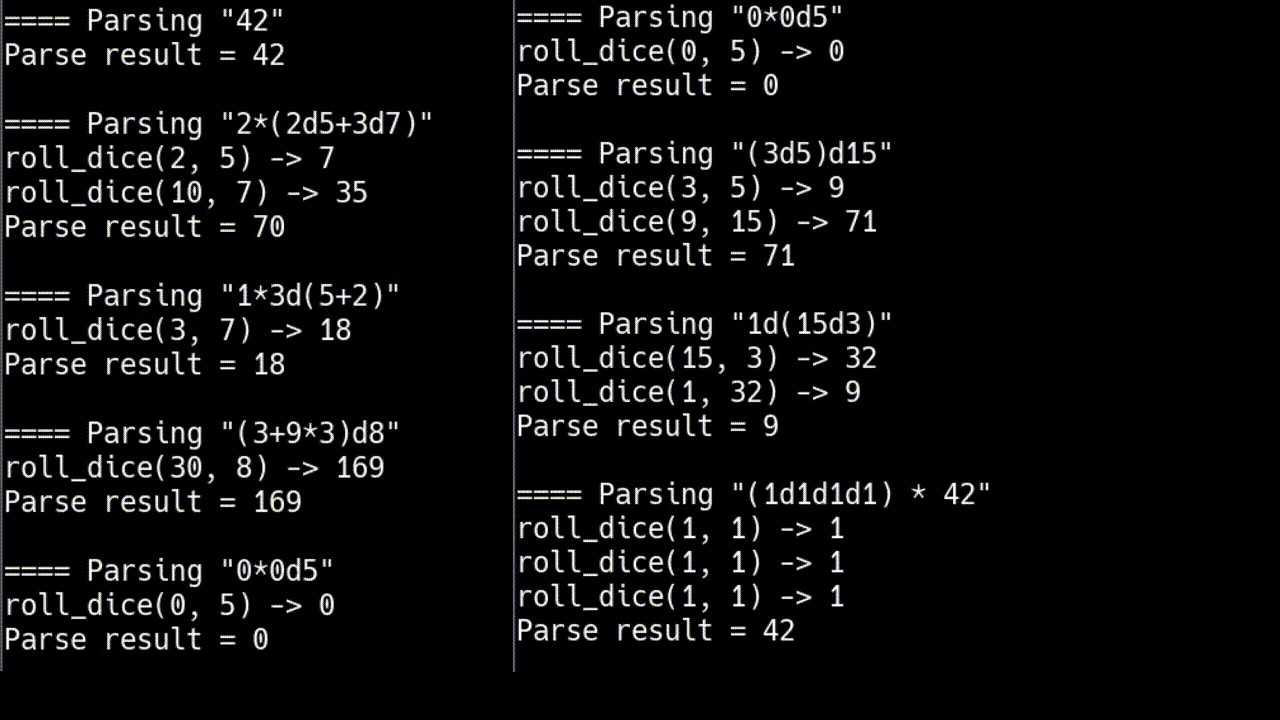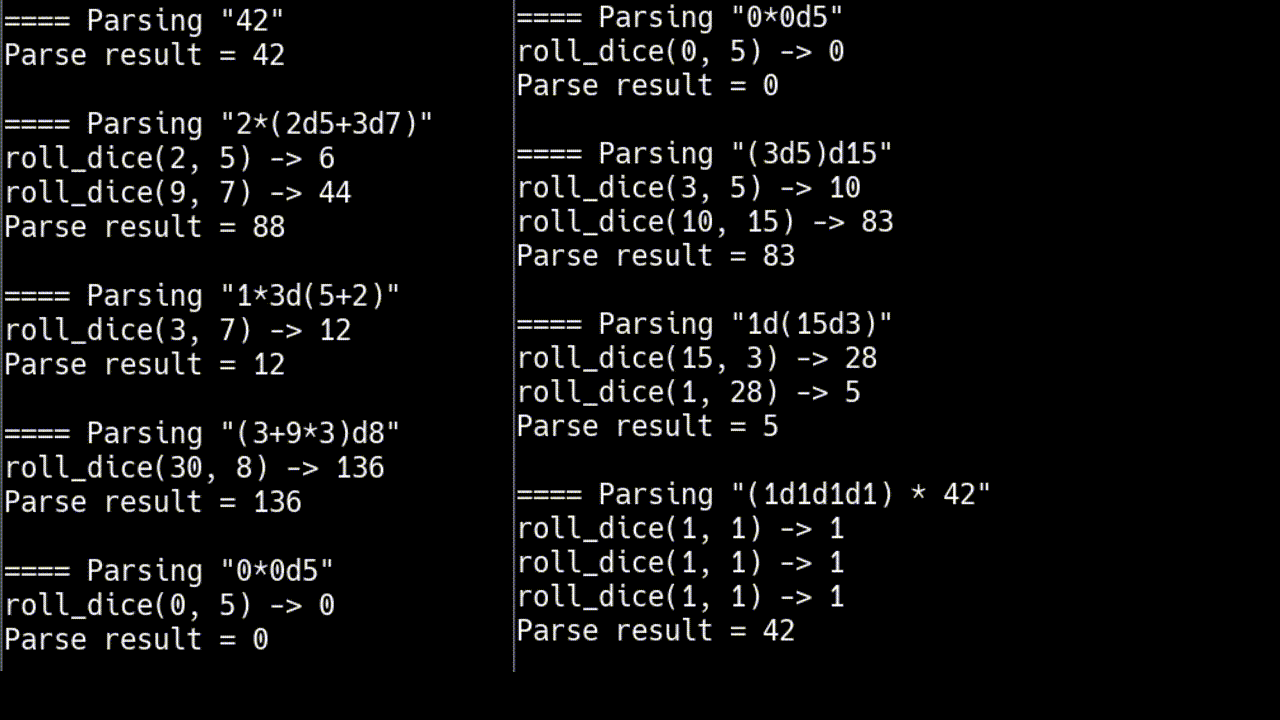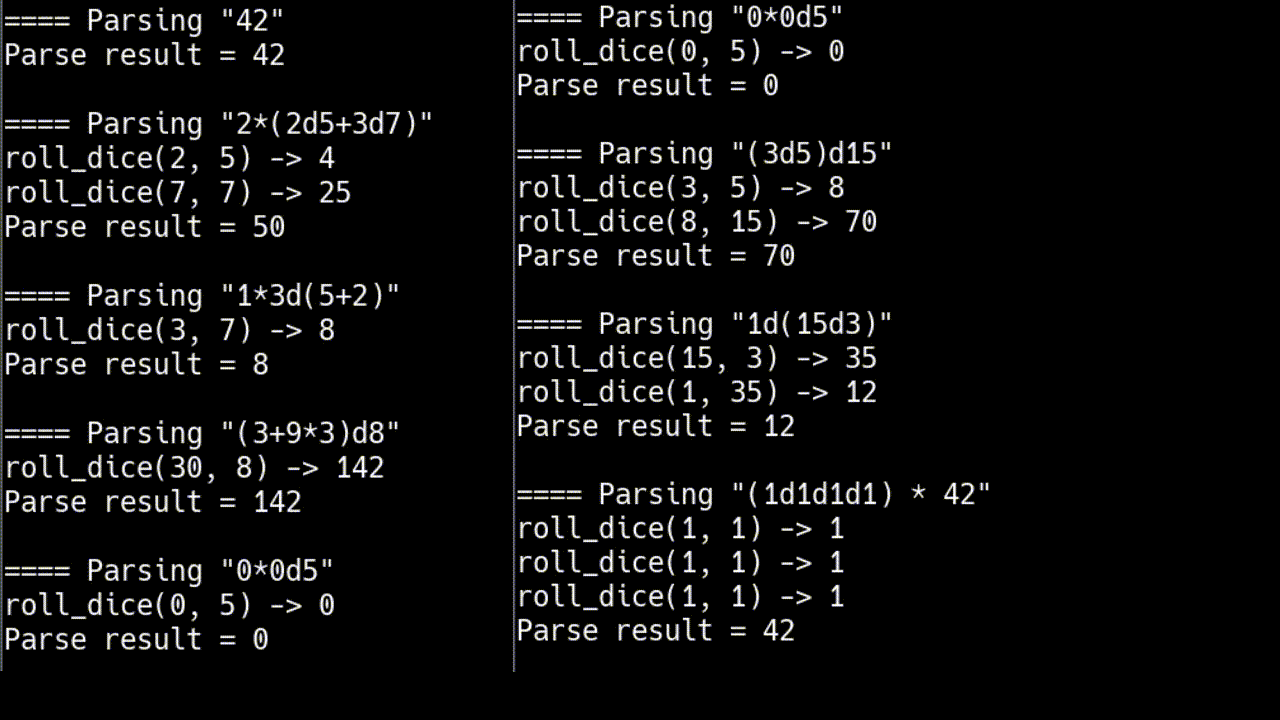
¹你不喜欢 C++ 吗?
关于c++ - 如何在 Boost.Spirit 语义 Action 中获得函数结果,我们在Stack Overflow上找到一个类似的问题: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62406805/